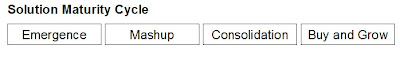
I saw the news about Informatica’s acquisition of Identity Systems, and it got me thinking. I recognize a familiar pattern that all too often occurs in the enterprise software business. I’m going to call it the Solution Maturity Cycle. It goes something like this:
1. The Emergence Phase: A young, fledgling company emerges that provides an excellent product that fills a need in the industry. This was Informatica in the 90’s. Rather than hand coding a system of metadata management, companies could use a cool graphical user interface to get the job done. Customers were happy. Informatica became a success. Life was good.
2. The Mashup Phase: Customers begin to realize that if they mash up the features of say, an ETL tool and a data quality tool, they can reap huge benefit for their companies. Eventually, the companies see the benefit of working together, and even begin to talk to prospective customers together. This was Informatica in 2003-5, working with FirstLogic and Trillium Software. Customers could decide which solution to use. Customers were happy that they could mashup, and happy that others had found success in doing so.
3. The Market Consolidation Phase: Under pressure from stockholders to increase revenue, the company looks to buy a solution in order to sell it in-house. The pressure also comes from industry analysts, who if they’re doing their job properly, interpret the mashup as a hole in the product. Unfortunately, the established and proven technology companies are too expensive to buy, so the company looks to a young, fledgling data quality company. The decision on which company to buy is more influenced by bean counters than technologists. Even if there are limitations on the fledgling’s technology, the sales force pushes hard to eliminate mashup implementations, so that annual maintenance revenue will be recognized. This is what happened with Informatica and Similarity Systems in my opinion. Early adopters are confused by this and fearful that their mashup might not be supported. Some customers fight to keep their mashups, some yield to the pressure and install the new solution.
4. Buy and Grow Phase: When bean counters select technology to support the solution, they usually get some product synergies wrong. Sure, the acquisition works from a revenue-generating perspective, but from the technology solution perspective, it is limited. The customers are at the same time under pressure from the mega-vendors, who want to own the whole enterprise. What to do? Buy more technology. It’ll fill the holes, keep the mega-vendor wolves at bay, and build more revenue.
The Solution Maturity Cycle is something that we all must pay attention to when dealing with vendors. For example, I’m seeing phase 3 this cycle occur in the SAP world, where SAP’s acquisition of Business Objects dropped several data quality solutions in SAP’s lap. Now despite the many successful mashups of Trillium Software and SAP, customers are being shown other solutions from the acquisition. All along, history makes me question whether an ERP vendor will be committed long term to the data quality market.
After a merger occurs, a critical decision point comes to customers. Should a customer resist pulling out mashups, or should you try to unify the solution under one vendor? It's a tough decision. The decision may affect internal IT teams, causing conflict between those who have been working on the mashup versus the mega-vendor team. In making this decision, there are a couple of key questions to ask:
- Is the newly acquired technology in the vendor’s core competency?
- Is the vendor committed to interoperability with other enterprise applications, or just their own? How will this affect your efforts for an enterprise-wide data governance program?
- Is the vendor committed to continual improvement this part of the solution?
- How big is the development team and how many people has the vendor hired from the purchased company? (Take names.)
- Can the vendor prove that taking out a successful solution to put in a new one will make you more successful?
- Are there any competing solutions within the vendor’s own company, poised to become the standard?
- Who has been successful with this solution, and do they have the same challenges that I have?



2 comments:
I think this is the first time I've seen it described this way, but you're correct, sir. There is a certain pattern to emerging technologies that tends to hurt the little guy. Since we don't have huge budgets at our company, it is difficult to keep up.
One weapon we do have to fight back when buying enterprise applications is the contract. If we can get assurances in the contract for continued support, at least we have something.
Steve, I wonder if your blog entry has anything to do with the Business Objects apology issued a few weeks ago.
Post a Comment